Abstract
The worldwide spread of the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has led to a global pandemic since its identification in Wuhan, China in December 2019.1 Few cases of COVID-19-associated dermatologic manifestations have been reported in the literature to date. This report describes the clinical features of a localized pruritic scarlatiniform rash of the ears and antecubital fossa on defervescence in a 29-year-old patient with COVID-19. Our case stands to further illuminate the dermatologic manifestations of this novel disease.
- Community Medicine
- COVID-19
- Dermatology
- Exanthema
- Family Medicine
- Itching
- Pandemics
- Primary Health Care
- Prurigo
- Pruritus
- Rash
- Scarlet Fever
Introduction
The rapid, worldwide spread of the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has led to a global pandemic since its identification in Wuhan, China in December 2019.1 The diagnosis is suspected clinically in patients who present with symptoms of fever, cough, dyspnea, myalgia, and fatigue and is confirmed via laboratory testing.2 Few cases of COVID-19-associated dermatologic manifestations have been reported in the literature to date. This report describes the clinical features of a cutaneous eruption of the ears and antecubital fossa in a patient with COVID-19.
Case Report
On 23 March 2020, a 29-year-old male health care worker presented to our outpatient clinic in Abilene, Texas with a 2-day history of sore throat and dry cough. He also reported new-onset fever, myalgia, and fatigue, which started the morning of presentation. The patient’s only significant dermatologic past medical history was alopecia areata, for which he received monthly intralesional steroid injections. His last injection was administered 1 month before presentation. He denied any recent travel or known sick contacts.
Physical examination revealed a body temperature of 38.8°C, pulse of 101 beats per minute, and oxygen saturation of 95% while the patient was breathing ambient air. His breathing was unlabored. Rapid antigen detection tests for influenza A, influenza B, and group A streptococci were negative. Given that the patient was a health care worker, a nasopharyngeal swab was obtained to test for SARS-CoV-2 via real-time reverse-transcriptase–polymerase-chain-reaction (rRT-PCR) assay and was subsequently positive. Given clinical stability, the patient was instructed to self-isolate at home, monitor for clinical progression with daily temperature checks, and continue supportive therapy.
The patient reported taking 1 dose of an over-the-counter cold medication containing acetaminophen, dextromethorphan, and doxylamine the night before presentation and then a single dose of acetaminophen monotherapy the following 2 nights for throat pain.
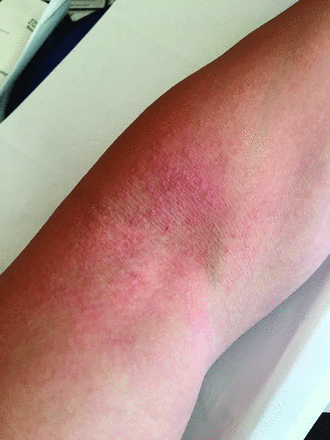
Two days after his initial presentation, day 5 of illness, the patient reported resolution of fevers and gradual improvement of his other presenting symptoms. He also noted the development of a pruritic, scarlatiniform, erythematous, papular eruption of the helical rim, antihelix, and earlobe. On day 6 of illness, the rash spread to circumferentially involve the elbows with greater involvement of the antecubital fossa (Figure 1). The rash gradually improved without therapy. By day 11 of illness, the eruption led to slight desquamation of the affected areas before complete resolution (Figure 2).
Image left elbow on day 11 of illness demonstrating a localized pruritic scarlatiniform of erythematous papules.
Image of the right ear demonstrating residual skin erythema and slight desquamation on day 11 of illness.
Discussion
Dermatologic manifestations of other coronaviruses have been previously reported in the literature.3,4 However, a complete understanding of the clinical spectrum of SARS-CoV-2 infection is still rapidly developing – ranging from asymptomatic carriers to acute respiratory distress syndrome and even death.1,5
Although SARS-COV-2 seems to have no demonstrated tropism for the skin,6 there have been reports of dermatologic manifestations of COVID-19 patients. Guan et al. report a case series of 1099 patients of which 2 patients (0.2%) had rashes that were not described further.7 Another case series from Lecco Hospital, Lombardo, Italy reports that of the 88 confirmed COVID-19 positive patients they examined, 18 patients (20.4%) had some form of cutaneous manifestation – erythematous rash, widespread urticaria, and varicella-like vesicles of primarily truncal distribution with low or absent pruritus.8 Case reports have also noted a dengue-like petechial rash as well as a morbilliform, maculopapular, nonpruritic rash as presenting symptoms in patients subsequently diagnosed with COVID-19.9,10 Additional reports discuss a transient nonpruritic livedoid eruption and acro-ischemia of the extremities mimicking perniosis.11⇓⇓–14 Hoenig et al describe a self-resolving, erythematous, slightly-edematous rash of the malar region, neck, and ears of a 26-year-old patient with presumptive COVID-19 based on close-contact exposure; however, due to shortages of SARS-CoV-2 testing kits, the patient was not tested.15 As had been noted with other coronaviruses,4 the dermatologic manifestations of Kawasaki disease in children have also been reported in association with SARS-CoV-2.16
Our patient’s history of alopecia areata and the treatment he was undergoing may warrant consideration as a confounding factor. However, neither the autoimmune disorder, which causes nonscarring hair loss nor intralesional steroid injections, which may cause atrophy of the skin at the site of injection, have been known to cause rashes in unaffected areas as described in our case.17
Our report illustrates a case of a pruritic scarlatiniform rash of the ears and antecubital fossa after defervescence in a patient with confirmed SARS-CoV-2. We feel our patient’s rash adds to the growing body of data for clinical features of COVID-19 and is worth sharing with the medical community. Additional research and case reports will help further clarify the full clinical spectrum of COVID-19.
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Kleesy Thomas and Audra Cochran for their expertise and assistance throughout all aspects of our case report and for their help in the critical review of our manuscript.
Notes
This article was externally peer reviewed.
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that there are no conflicting or competing interests.
To see this article online, please go to: http://jabfm.org/content/34/Supplement/S183.full.
- Received for publication April 17, 2020.
- Revision received May 28, 2020.
- Accepted for publication June 2, 2020.