Abstract
Background:
Overweight prevalence among children/adolescents is increasing, while adult obesity may potentially cause a decline in life expectancy. More exercise is uniformly recommended, although treatment efficacy remains unclear.
Objective:
To determine the efficacy of exercise alone for treating overweight in children/adolescents.
Design:
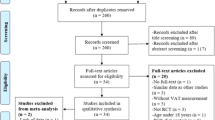
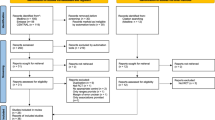
A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials published in English were completed following multiple database searches performed on December 10, 2004. Studies of isolated or adjunctive exercise/physical activity treatment in overweight/obese children or adolescents which reported any overweight outcome were included. Literature searches identified 645 papers which were manually searched, of which 45 were considered for inclusion, of which 13 papers which reported 14 studies were included (N=481 overweight boys and girls, aged ∼12 years). Two reviewers independently identified relevant papers for potential inclusion and assessed methodological quality. Principal measures of effects included the mean difference (MD) (between treatment and control groups), the weighted MD (WMD), and the standardized MD (SMD).
Results:
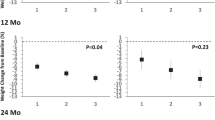
Few studies were of robust design. The pooled SMD was −0.4 (−0.7, −0.1, P=0.006) for percent body fat, and −0.2 (−0.6, 0.1, P=0.07) for central obesity outcomes, whereas the pooled WMD was −2.7 kg (−6.1 kg, 0.8 kg, P=0.07) for body weight, all of which favored exercise. Pooled effects on body weight were significant and larger for studies of higher doses, whereas nonsignificant and smaller effects were seen for studies of lower doses of exercise (155–180 min/weeks vs 120–150 min/weeks).
Conclusions:
Based on the small number of short-term randomized trials currently available, an aerobic exercise prescription of 155–180 min/weeks at moderate-to-high intensity is effective for reducing body fat in overweight children/adolescents, but effects on body weight and central obesity are inconclusive. Recommendations for future study designs are discussed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chinn S, Rona RJ . Prevalence and trends in overweight and obesity in three cross sectional studies of British Children, 1974–94. BMJ 2001; 322: 24–26.
Moreno LA, Sarria A, Fleta J, Rodriguez G, Bueno M . Trends in body mass index and overweight prevalence among children and adolescents in the region of Aragon (Spain) from 1985 to 1995. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord: J Int Assoc Study Obes 2000; 24: 925–931.
Freedman DS, Srinivasan SR, Valdez RA, Williamson DF, Berenson GS . Secular increases in relative weight and adiposity among children over two decades: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Pediatrics 1997; 99: 420–426.
Troiano RP, Flegal KM, Kuczmarski RJ, Campbell SM, Johnson CL . Overweight prevalence and trends for children and adolescents. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 1963 to 1991. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1995; 149: 1085–1091.
Booth ML, Chey T, Wake M, Norton K, Hesketh K, Dollman J et al. Change in the prevalence of overweight and obesity among young Australians, 1969–1997. Am J Clin Nutr 2003; 77: 29–36.
Britz B, Siegfried W, Ziegler A, Lamertz C, Herpertz-Dahlmann BM, Remschmidt H et al. Rates of psychiatric disorders in a clinical study group of adolescents with extreme obesity and in obese adolescents ascertained via a population based study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord: J Int Assoc Study Obes 2000; 24: 1707–1714.
Erickson SJ, Robinson TN, Haydel KF, Killen JD . Are overweight children unhappy?: Body mass index, depressive symptoms, and overweight concerns in elementary school children. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2000; 154: 931–935.
Zametkin AJ, Zoon CK, Klein HW, Munson S . Psychiatric aspects of child and adolescent obesity: a review of the past 10 years. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatr 2004; 43: 134–150.
McMurray RG, Harrel JS, Levine AA, Gansky SA . Childhood obesity elevates blood pressure and total cholesterol independent of physical activity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord: J Int Assoc Study Obes 1995; 19: 881–886.
Weiss R, Dziura J, Burgert TS, Tamborlane WV, Taksali SE, Yeckel CW et al. Obesity and the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 2362–2374.
Reich A, Muller G, Gelbrich G, Deutscher K, Godicke R, Kiess W . Obesity and blood pressure – results from the examination of 2365 schoolchildren in Germany. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord: J Int Assoc Study Obes 2003; 27: 1459–1464.
Dietz WH . Overweight in childhood and adolescence. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 855–857.
Cook S, Weitzman M, Auinger P, Nguyen M, Dietz WH . Prevalence of a metabolic syndrome phenotype in adolescents: findings from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1994. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2003; 157: 821–827.
Pinhas-Hamiel O, Dolan LM, Daniels SR, Standiford D, Khoury PR, Zeitler P . Increased incidence of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus among adolescents. J Pediatr 1996; 128: 608–615.
Murray CJ, Lopez AD . Alternative projections of mortality and disability by cause 1990–2020: Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 1997; 349: 1498–1504.
Olshansky SJ, Passaro DJ, Hershow RC, Layden J, Carnes BA, Brody J et al. A potential decline in life expectancy in the United States in the 21st century. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 1138–1145.
Dietz WH, Gortmaker SL . Preventing obesity in children and adolescents. Ann Rev Publ Health 2001; 22: 337–353.
Kumanyika SK . Minisymposium on obesity: overview and some strategic considerations. Ann Rev Public Health 2001; 22: 293–308.
Blair SN, Nichaman MZ . The public health problem of increasing prevalence rates of obesity and what should be done about it. Mayo Clin Proc 2002; 77: 109–113.
Jakicic JM, Clark K, Coleman E, Donnelly JE, Foreyt J, Melanson E et al. American college of sports medicine position stand. Appropriate intervention strategies for weight loss and prevention of weight regain for adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2001; 33: 2145–2156.
National Health and Medical Research Council. Draft National Clinical Guidelines for Weight Control and Obesity Management in Children and Adolescents. Canberra: NHMRC, 2002. pp 1–94.
Campbell K, Waters E, O’Meara S, Summerbell C . Interventions for preventing obesity in childhood. A systematic review. Obes Rev 2001; 2: 149–157.
Campbell K, Waters E, O’Meara S, Kelly S, Summerbell C . Interventions for treating obesity in children. Cochr Database Syst Rev 2004; 4.
LeMura LM, Maziekas MT . Factors that alter body fat, body mass, and fat-free mass in pediatric obesity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2002; 34: 487–496.
Coates TJ, Thoresen CE . Treating obesity in children and adolescents: a review. Am J Publ Health 1978; 68: 143.
Lobstein T, Baur L, Uauy R . Obesity in children and young people: a crisis in public health. Obes Rev 2004; 5: 4–85.
Summerbell CD, Ashton V, Campbell KJ, Edmunds L, Kelly S, Waters E . Interventions for treating obesity in children. Cochr Database Syst Rev 2003; 3, C0001872.
Egger M, Smith GD, Altman DG . Systematic Reviews in Health Care: Meta-Analysis in Context. BMJ Publishing: London, 2001.
Gutin B, Owens S, Slavens G, Riggs S, Treiber F . Effect of physical training on heart-period variability in obese children. J Pediatr 1997; 130: 938–943.
Gutin B, Barbeau P, Owens S, Lemmon CR, Bauman M, Allison J et al. Effects of exercise intensity on cardiovascular fitness, total body composition, and visceral adiposity of obese adolescents. Am J Clin Nutr 2002; 75: 818–826.
Dwyer T, Coonan WE, Leitch DR, Hetzel BS, Baghurst RA . An investigation of the effects of daily physical activity on the health of primary school students in South Australia. Int J Epidemiol 1983; 12: 308–313.
Vandongen R, Jenner DA, Thompson C, Taggart AC, Spickett EE, Burke V et al. A controlled evaluation of a fitness and nutrition intervention program on cardiovascular health in 10- to 12-year-old children. Prev Med 1995; 24: 9–22.
Sallis JF, McKenzie TL, Alcaraz JE, Kolody B, Faucette N, Hovell MF . The effects of a 2-year physical education program (SPARK) on physical activity and fitness in elementary school students. Sports, Play and Active Recreation for Kids. Am J Public Health 1997; 87: 1328–1334.
Morris FL, Naughton GA, Gibbs JL, Carlson JS, Wark JD . Prospective ten-month exercise intervention in premenarcheal girls: positive effects on bone and lean mass. J Bone Mineral Res 1997; 12: 1453–1462.
Mo-suwan L, Pongprapai S, Junjana C, Puetpaiboon A . Effects of a controlled trial of a school-based exercise program on the obesity indexes of preschool children. Am J Clin Nutr 1998; 68: 1006–1011.
McKay HA, Petit MA, Schutz RW, Prior JC, Barr SI, Khan KM . Augmented trochanteric bone mineral density after modified physical education classes: a randomized school-based exercise intervention study in prepubescent and early pubescent children. J Pediatr 2000; 136: 156–162.
Warren JM, Henry CJ, Lightowler HJ, Bradshaw SM, Perwaiz S . Evaluation of a pilot school programme aimed at the prevention of obesity in children. Health Promotion Int 2003; 18: 287–296.
Williford HN, Blessing DL, Duey WJ, Barksdale JM, Wang N, Olson MS et al. Exercise training in black adolescents: changes in blood lipids and Vo2max. Ethnicity Dis 1996; 6: 279–285.
Tolfrey K, Campbell IG, Batterham AM . Exercise training induced alterations in prepubertal children's lipid-lipoprotein profile. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1998; 30: 1684–1692.
Eliakim A, Makowski GS, Brasel JA, Cooper DM . Adiposity, lipid levels, and brief endurance training in nonobese adolescent males. Int J Sports Med 2000; 21: 332–337.
Nichols DL, Sanborn CF, Love AM . Resistance training and bone mineral density in adolescent females. J Pediatr 2001; 139: 494–500.
Kahle EB, O'Dorisio TM, Walker RB, Eisenman PA, Reiser S, Cataland S et al. Exercise adaptation responses for gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) and insulin in obese children. Possible extra-pancreatic effects. Diabetes 1986; 35: 579–582.
Huttunen NP, Knip M, Paavilainen T . Physical activity and fitness in obese children. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1986; 10: 519–525.
Nichols JF, Bigelow DM, Canine KM . Short-term weight loss and exercise training effects on glucose-induced thermogenesis in obese adolescent males during hypocaloric feeding. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1989; 13: 683–690.
Hayashi T, Fujino M, Shindo M, Hiroki T, Arakawa K . Echocardiographic and electrocardiographic measures in obese children after an exercise program. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1987; 11: 465–472.
Treuth MS, Hunter GR, Figueroa-Colon R, Goran MI . Effects of strength training on intra-abdominal adipose tissue in obese prepubertal girls. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1998; 30: 1738–1743.
Widhalm K, Maxa E, Zyman H . Effect of diet and exercise upon the cholesterol and triglyceride content of plasma lipoproteins in overweight children. Eur J Pediatr 1978; 127: 121–126.
Pena M, Barta L, Regoly-Merei A, Tichy M . The influence of physical exercise upon the body composition of obese children. Acta Paediatr Acad Sci Hungari 1980; 21: 9–14.
Reybrouck T, Vinckx J, Van den Berghe G, Vanderschueren-Lodeweyckx M . Exercise therapy and hypocaloric diet in the treatment of obese children and adolescents. Acta Paediatr Scand 1990; 79: 84–89.
Jette M, Barry W, Pearlman L . The effects of an extracurricular physical activity program on obese adolescents. Canad J Publ Health Rev Canad Sante Publ 1977; 68: 39–42.
Gutin B, Cucuzzo N, Islam S, Smith C, Moffatt R, Pargman D . Physical training improves body composition of black obese 7- to 11-year-old girls. Obes Res 1995; 3: 305–312.
Pena M, Bacallao J, Barta L, Amador M, Johnston FE . Fiber and exercise in the treatment of obese adolescents. J Adolesc Health Care 1989; 10: 30–34.
Kang HS, Gutin B, Barbeau P, Owens S, Lemmon CR, Allison J et al. Physical training improves insulin resistance syndrome markers in obese adolescents. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2002; 34: 1920–1927.
Barbeau P, Gutin B, Litaker M, Owens S, Riggs S, Okuyama T . Correlates of individual differences in body-composition changes resulting from physical training in obese children. Am J Clin Nutr 1999; 69: 705–711.
Barbeau P, Gutin B, Litaker MS, Ramsey LT, Cannady WE, Allison J et al. Influence of physical training on plasma leptin in obese youths. Canad J Appl Physiol 2003; 28: 382–396.
Mitchell BM, Gutin B, Kapuku G, Barbeau P, Humphries MC, Owens S et al. Left ventricular structure and function in obese adolescents: relations to cardiovascular fitness, percent body fat, and visceral adiposity, and effects of physical training. Pediatrics 2002; 109: e73.
Gutin B, Ramsey L, Barbeau P, Cannady W, Ferguson M, Litaker M et al. Plasma leptin concentrations in obese children: changes during 4-mo periods with and without physical training. Am J Clin Nutr 1999; 69: 388–394.
Gutin B, Cucuzzo N, Islam S, Smith C, Stachura ME . Physical training, lifestyle education, and coronary risk factors in obese girls. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1996; 28: 19–23.
Gutin B, Owens S, Okuyama T, Riggs S, Ferguson M, Litaker M . Effect of physical training and its cessation on percent fat and bone density of children with obesity. Obes Res 1999; 7: 208–214.
Humphries MC, Gutin B, Barbeau P, Vemulapalli S, Allison J, Owens S . Relations of adiposity and effects of training on the left ventricle in obese youths. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2002; 34: 1428–1435.
Sung RY, Yu CW, Chang SK, Mo SW, Woo KS, Lam CW . Effects of dietary intervention and strength training on blood lipid level in obese children. Arch Dis Child 2002; 86: 407–410.
Ferguson MA, Gutin B, Le NA, Karp W, Litaker M, Humphries M et al. Effects of exercise training and its cessation on components of the insulin resistance syndrome in obese children. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord J Int Assoc Study Obes 1999; 23: 889–895.
Woo KS, Chook P, Yu CW, Sung RY, Qiao M, Leung SS et al. Effects of diet and exercise on obesity-related vascular dysfunction in children. Circulation 2004; 109: 1981–1986.
Emes C, Velde B, Moreau M, Murdoch DD, Trussell R . An activity based weight control program. Adapt Phys Activity Quart 1990; 7: 314–324.
Faith MS, Berman N, Heo M, Pietrobelli A, Gallagher D, Epstein LH et al. Effects of contingent television on physical activity and television viewing in obese children. Pediatrics 2001; 107: 1043–1048.
Blomquist B, Borjeson M, Larsson Y, Persson B, Sterky G . The effect of physical activity on the body measurements and work capacity of overweight boys. Acta Paediatr Scand 1965; 54: 566–572.
Epstein LH, Wing RR, Penner BC, Kress MJ . Effect of diet and controlled exercise on weight loss in obese children. J Pediatr 1985; 107: 358–361.
Becque MD, Katch VL, Rocchini AP, Marks CR, Moorehead C . Coronary risk incidence of obese adolescents: reduction by exercise plus diet intervention. Pediatrics 1988; 81: 605–612.
Hills AP, Parker AW . Obesity management via diet and exercise intervention. Child Care Health Dev 1988; 14: 409–416.
Katch V, Becque MD, Marks C, Moorehead C, Rocchini A . Basal metabolism of obese adolescents: inconsistent diet and exercise effects. Am J Clin Nutr 1988; 48: 565–569.
Rocchini AP, Katch V, Anderson J, Hinderliter J, Becque D, Martin M et al. Blood pressure in obese adolescents: effect of weight loss. Pediatrics 1988; 82: 16–23.
Schwingshandl J, Sudi K, Eibl B, Wallner S, Borkenstein M . Effect of an individualised training programme during weight reduction on body composition: a randomised trial. Arch Dis Childhood 1999; 81: 426–428.
Saris WH, Blair SN, van Baak MA, Eaton SB, Davies PS, Di Pietro L et al. How much physical activity is enough to prevent unhealthy weight gain? Outcome of the IASO 1st Stock Conference and consensus statement. Obes Rev 2003; 4: 101–114.
Daniels SR, Arnett DK, Eckel RH, Gidding SS, Hayman LL, Kumanyika S et al. Overweight in children and adolescents: pathophysiology, consequences, prevention, and treatment. Circulation 2005; 111: 1999–2012.
USDA. Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2005. http://www.healthierus.gov/dietaryguidelines/, (accessed 20 July, 2005).
Bar-Or O, Foreyt J, Bouchard C, Brownell KD, Dietz WH, Ravussin E et al. Physical activity, genetic, and nutritional considerations in childhood weight management. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1998; 30: 2–10.
Arluk SL, Branch JD, Swain DP, Dowling EA . Childhood obesity's relationship to time spent in sedentary behavior. Military Med 2003; 168: 583–586.
Crespo CJ, Smit E, Troiano RP, Bartlett SJ, Macera CA, Andersen RE . Television watching, energy intake, and obesity in US children: results from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1994. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2001; 155: 360–365.
Maffeis C, Talamini G, Tato L . Influence of diet, physical activity and parents' obesity on children's adiposity: a four-year longitudinal study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord: J Int Assoc Study Obes 1998; 22: 758–764.
Proctor MH, Moore LL, Gao D, Cupples LA, Bradlee ML, Hood MY et al. Television viewing and change in body fat from preschool to early adolescence: The Framingham Children's Study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord: J Int Assoc Study Obes 2003; 27: 827–833.
Bouziotas C, Koutedakis Y, Nevill A, Ageli E, Tsigilis N, Nikolaou A et al. Greek adolescents, fitness, fatness, fat intake, activity, and coronary heart disease risk. Arch Dis Childhood 2004; 89: 41–44.
O'Loughlin J, Gray-Donald K, Paradis G, Meshefedjian G . One- and two-year predictors of excess weight gain among elementary schoolchildren in multiethnic, low-income, inner-city neighborhoods. Am J Epidemiol 2000; 152: 739–746.
Hernandez B, Gortmaker SL, Colditz GA, Peterson KE, Laird NM, Parra-Cabrera S . Association of obesity with physical activity, television programs and other forms of video viewing among children in Mexico city. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord: J Int Assoc Study Obes 1999; 23: 845–854.
Patrick K, Norman GJ, Calfas KJ, Sallis JF, Zabinski MF, Rupp J et al. Diet, physical activity, and sedentary behaviors as risk factors for overweight in adolescence. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2004; 158: 385–390.
Miller WC, Koceja DM, Hamilton EJ . A meta-analysis of the past 25 years of weight loss research using diet, exercise or diet plus exercise intervention. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord: J Int Assoc Study Obes 1997; 21: 941–947.
Centre for R, Dissemination. A meta-analysis of the past 25 years of weight loss research using diet, exercise or diet plus exercise intervention (structured abstract). Database Abstr Rev Effectiv 2005; 2: 2.
Ekelund U, Yngve A, Brage S, Westerterp K, Sjostrom M . Body movement and physical activity energy expenditure in children and adolescents: how to adjust for differences in body size and age. Am J Clin Nutr 2004; 79: 851–856.
Roemmich JN, Clark PA, Walter K, Patrie J, Weltman A, Rogol AD . Pubertal alterations in growth and body composition. V. Energy expenditure, adiposity, and fat distribution. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2000; 279: E1426–E1436.
Guo SS, Chumlea WC, Roche AF, Siervogel RM . Age- and maturity-related changes in body composition during adolescence into adulthood: the Fels Longitudinal Study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord: J Int Assoc Study Obes 1997; 21: 1167–1175.
Kraemer WJ, Volek JS, Clark KL, Gordon SE, Puhl SM, Koziris LP et al. Influence of exercise training on physiological and performance changes with weight loss in men. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1999; 31: 1320–1329.
Bryner RW, Ullrich IH, Sauers J, Donley D, Hornsby G, Kolar M et al. Effects of resistance vs. aerobic training combined with an 800 calorie liquid diet on lean body mass and resting metabolic rate. J Am Coll Nutr 1999; 18: 115–121.
Geliebter A, Maher MM, Gerace L, Gutin B, Heymsfield SB, Hashim SA . Effects of strength or aerobic training on body composition, resting metabolic rate, and peak oxygen consumption in obese dieting subjects. Am J Clin Nutr 1997; 66: 557–563.
Sweeney ME, Hill JO, Heller PA, Baney R, DiGirolamo M . Severe vs moderate energy restriction with and without exercise in the treatment of obesity: efficiency of weight loss. Am J Clin Nutr 1993; 57: 127–134.
Ross R, Dagnone D, Jones PJ, Smith H, Paddags A, Hudson R et al. Reduction in obesity and related comorbid conditions after diet-induced weight loss or exercise-induced weight loss in men. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Int Med 2000; 133: 92–103.
Pritchard JE, Nowson CA, Wark JD . A worksite program for overweight middle-aged men achieves lesser weight loss with exercise than with dietary change. J Am Diet Assoc 1997; 97: 37–42.
Treuth MS, Ryan AS, Pratley RE, Rubin MA, Miller JP, Nicklas BJ et al. Effects of strength training on total and regional body composition in older men. J Appl Physiol 1994; 77: 614–620.
Park SK, Park JH, Kwon YC, Kim HS, Yoon MS, Park HT . The effect of combined aerobic and resistance exercise training on abdominal fat in obese middle-aged women. J Physiol Anthropol Appl Hum Sci 2003; 22: 129–135.
Smith SR, Zachwieja JJ . Visceral adipose tissue: a critical review of intervention strategies. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord: J Int Assoc Study Obes 1999; 23: 329–335.
Cruz ML, Goran MI . The metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. Curr Diabet Rep 2004; 4: 53–62.
Duncan GE, Li SM, Zhou XH . Prevalence and trends of a metabolic syndrome phenotype among US adolescents, 1999–2000. Diabet Care 2004; 27: 2438–2443.
Ku CY, Gower BA, Hunter GR, Goran MI . Racial differences in insulin secretion and sensitivity in prepubertal children: role of physical fitness and physical activity. Obes Res 2000; 8: 506–515.
Brage S, Wedderkopp N, Ekelund U, Franks PW, Wareham NJ, Andersen LB et al. Features of the metabolic syndrome are associated with objectively measured physical activity and fitness in Danish children: the European Youth Heart Study (EYHS). Diabet Care 2004; 27: 2141–2148.
Begg CP, Cho MP, Eastwood SELSD, Horton RMB, Moher DM, Olkin IP et al. Improving the quality of reporting of randomized controlled trials: the CONSORT statement. JAMA 1996: 276:637–639.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atlantis, E., Barnes, E. & Singh, M. Efficacy of exercise for treating overweight in children and adolescents: a systematic review. Int J Obes 30, 1027–1040 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803286
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803286
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Prevention and treatment of childhood and adolescent obesity: a systematic review of meta-analyses
World Journal of Pediatrics (2019)
-
Racial/Ethnic Disparities: a Longitudinal Study of Growth Trajectories Among US Kindergarten Children
Journal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities (2018)
-
Effect of High-Intensity Interval Training on Fitness, Fat Mass and Cardiometabolic Biomarkers in Children with Obesity: A Randomised Controlled Trial
Sports Medicine (2018)
-
Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of pediatric obesity: consensus position statement of the Italian Society for Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetology and the Italian Society of Pediatrics
Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2018)
-
Risk Factors for Overweight in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder
Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities (2017)