Abstract
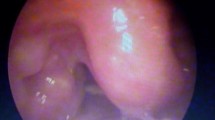
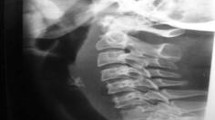
Retropharyngeal calcific tendinitis is an inflammatory process caused by calcium hydroxyapatite crystal deposition in the longus colli tendon of the prevertebral space, and it may mimic a retropharyngeal infection or abscess. The diagnosis of retropharyngeal calcific tendinitis will be made radiologically by the detection of calcifications anterior to C1–C3 and prevertebral soft tissue swelling. We present a case of acute retropharyngeal calcific tendinitis with an unusual location of calcification anterior to the C5–C6 disc.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Omezzine SJ, Hafsa C, Lahmar I, Driss N, Hamza H. Calcific tendinitis of the longus colli: diagnosis by CT. Joint Bone Spine. 2008;75:90–1.
Eastwood JD, Hudgins PA, Malone D. Retropharyngeal effusion in acute calcific prevertebral tendinitis: diagnosis with CT and MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998;19:1789–92.
Offiah CE, Hall E. Acute calcific tendinitis of the longus colli muscle: spectrum of CT appearances and anatomical correlation. Br J Radiol. 2009;82:e117–21.
Southwell K, Hornibrook J, O’Neill-Kerr D. Acute longus colli calcific tendonitis causing neck pain and dysphagia. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008;138:405–6.
Smith RV, Rinaldi J, Hood DR, Troost T. Hydroxyapatite deposition disease: an uncommon cause of acute odynophagia. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1996;114:321–3.
Mihmanli I, Karaarslan E, Kanberoglu K. Inflammation of vertebral bone associated with acute calcific tendinitis of the longus colli muscle. Neuroradiology. 2001;43:1098–101.
Hall FM, Docken WP, Curtis HW. Calcific tendinitis of the longus colli: diagnosis by CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1986;147:742–3.
De Maeseneer M, Vreugde S, Laureys S, Sartoris DJ, De Ridder F, Osteaux M. Calcific tendinitis of the longus colli muscle. Head Neck. 1997;19:545–8.
Chung T, Rebello R, Gooden EA. Retropharyngeal calcific tendinitis: case report and review of literature. Emerg Radiol. 2005;11:375–80.
Haun CL. Retropharyngeal tendinitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1978;130:1137–40.
Ring D, Vaccaro AR, Scuderi G, Pathria MN, Garfin SR. Acute calcific retropharyngeal tendinitis. Clinical presentation and pathological characterization. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76:1636–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S.Y., Jin, W., Lee, S.H. et al. Acute retropharyngeal calcific tendinitis: a case report with unusual location of calcification. Skeletal Radiol 39, 817–820 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-010-0879-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-010-0879-3