Abstract
Introduction: There are a number of well-established barriers to accessing primary care. The LINKED Study set out to improve primary care usage through 1-on-1 counseling and referrals for patients with diabetes being treated at local free clinics. We hypothesized that this educational intervention paired with expedited referral would increase the use of federally qualified health centers (FQHCs) as a source of health care and ultimately lead to improved diabetic health.
Methods: Medical student volunteers counseled participants on the importance of primary care. The participants then completed surveys about diabetic health, socioeconomic status, and general demographics. Participants were subsequently assigned to 1 of 2 FQHCs; designated care coordinators facilitated appointments. At the end of a 9-month action period, participants repeated the initial surveys, now including appointment history and health data (hemoglobin A1c (%) [HbA1c], body mass index).
Results: Sixty-eight participants were enrolled. The average time since a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus was 8.3 years (standard deviation [SD], 8.4 years), and 25% of participants used insulin. Mean baseline HbA1c for participants with a recorded value (n = 55) was 9.5 (SD, 2.5). FQHC appointments were scheduled by 68% of participants; 38% of the participants attended ≥2 appointments. The most common reported barriers to accessing primary care were no prior health insurance (85.3%) and cost of medical care (72.1%). In our follow-up assessment there was a statistically significant decrease in HbA1c for those linked to FQHCs (9.5 [SD, 2.3] to 8.3 [SD, 2.2]; n = 21).
Conclusions: This study demonstrates the utility of a linkage program from free clinics to FQHCs. Those individuals with diabetes receiving health care from an FQHC demonstrated improved glycemic control.
- Community Health Centers
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Glycated Hemoglobins
- Populations
- Underserved
- Social Determinants of Health
Diabetes is a chronic condition best managed with continuous, quality care.1 It is estimated that by 2020, more than half of the American adult population will have either diabetes or prediabetes, with associated health care costs approaching $500 billion.2 The prevalence of diabetes and the rate of complications resulting from poor diabetic health are highest among those who are uninsured, have a lower socioeconomic status (SES), and are of a minority race.3⇓–5
Several theories have been proposed to explain the disparity in diabetes prevalence and management that occurs among those with a lower SES, including decreased use of continuous, quality health care resources.5 Safety-net (free) clinics provide medical care to those who would otherwise be unable to access it.4⇓–6 These clinics are often primarily designed for acute care services but have become major providers of chronic disease management as the prevalence of these conditions increases. In addition, their level of patient care fluctuates based on the availability of physician oversight, adequate facilities, and medical supplies.7
Federally qualified health centers (FQHCs) qualify for funding under Section 330 of the Public Health Services Act and enhanced reimbursement from Medicare and Medicaid. These centers must serve underserved populations, offer a sliding fee scale, and provide comprehensive services. Studies have highlighted the importance of primary care physicians (PCPs) in improving glycemic control and in reducing diabetic sequelae through educational interventions, drug therapy, exercise regimens, and dietary changes.1,8,9 This suggests that linking high-risk individuals who frequently access care at local free clinics to FQHCs could improve their diabetic health.
There are a number of well-established barriers to accessing primary care, including a lack of awareness of resources, difficulty scheduling within a workday, trouble finding child care, costs of therapy and medical care, and lack of transportation.5 Noting these barriers, we set out to improve primary care usage through 1-on-1 counseling and referrals for patients with diabetes treated at local free clinics. We hypothesized that educational intervention paired with an expedited referral would increase the use of FQHCs and lead to improved diabetic health.
Methods
Recruitment
This was a prospective study conducted by medical students at The Ohio State University College of Medicine in partnership with 2 local free clinics and 2 local FQHCs. This study was approved by The Ohio State University Institutional Review Board (protocol no. 2012H0266).
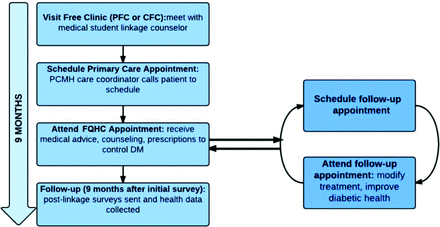
Participants were recruited to the Longitudinal Intervention: Networking Care and Educating for Diabetes (LINKED) study from 2 free clinics in Columbus, Ohio: the Physicians Care Connection (PCC) (formerly known as Physicians Free Clinic [PFC]) and the Columbus Free Clinic (CFC). The recruitment occurred from January 2013 to February 2014, and follow-up occurred 9 months after each participant's recruitment date. Inclusion criteria consisted of an existing diagnosis of type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM), English or Spanish as the primary language, age >18 years, and seeking medical care at the PFC or CFC. Figure 1 outlines the LINKED study design.
LINKED Study Design. Patients were enrolled in the LINKED Study at the Physicians Free Clinic (PFC) or the Columbus Free Clinic (CFC) through a counseling session conducted by a medical student. Information regarding current health status was obtained through an initial survey. Contact information was provided to federally qualified health center (FQHC) care coordinators to arrange appointments. Participants were contacted again after 9 months to complete postlinkage surveys, and their charts were reviewed at the free clinics and FQHCs for outcome data. DM, diabetes mellitus; PCMH, patient-centered medical home.
Educational Intervention, Referral, and Survey Processes
Participants were recruited and gave consent during their clinic visit at the PFC or CFC, during which they participated in a 1-on-1 educational intervention about the advantage of primary care in managing their diabetes and preventing long-term diabetic health complications; the interventions were conducted by medical students. The educational focal points included (1) the advantage of continuity of care in establishing a relationship with a PCP; (2) decreased wait time and expedited scheduling at a FQHC compared with local free clinics; (3) greater variety and availability of medications compared with free clinics; and (4) federally subsidized cost and insurance requirements at FQHCs. During this initial encounter, participants completed surveys capturing demographics, financial and socioeconomic status, food security, PCP use, and diabetic health maintenance behaviors.
Participants were linked to 1 of 2 FQHCs: the Lower Lights Christian Health Center or PrimaryOne Health, formerly known as Columbus Neighborhood Health Center. These 2 FQHCs are also recognized as level 3 patient-centered medical homes by the National Committee for Quality Assurance. At the time of the study, the Lower Lights Christian Health Center had 1 office and the Columbus Neighborhood Health Center had 6 local offices. To minimize travel, participants were assigned to the FQHC closest to their homes.
Within 1 week of their recruitment, participants were contacted by phone by assigned FQHC care coordinators. The first available appointments were often within 2 to 5 days. After recruitment to the study, patients started a 9-month action period with no further communication from the medical student LINKED team. After 9 months, surveys similar to the initial recruitment surveys were sent to participants. Appointment history and health data (eg, hemoglobin A1c [HbA1c], body mass index [BMI]) after linkage were collected from patient charts at the FQHCs and free clinics. Hereafter the FQHCs are referred to as FQHC1 and FQHC2.
Data Analysis
Survey data were gathered through the REDCap system.10 Two-tailed paired t tests of participant data with matched values before and after the action period were used to assess change in HbA1c and BMI (intragroup comparison); 2-tailed 2-sample t tests were used to evaluate outcomes between participants attending ≥2 versus <2 FQHC appointments and outcomes between FQHCs (intergroup comparisons); and χ2 tests were used to evaluate linkage rate and other outcomes of categorical variables.
Results
General Demographics and Socioeconomic Status
A summary of baseline data, including demographics and SES, is presented in Table 1.
Summary of Baseline Data*
Health Data
Average time since a diagnosis of DM was 8.3 years (range, 0.04–30 years), and 25% of participants used insulin. Among participants with a recorded HbA1c value in their free clinic medical records (n = 55), the baseline HbA1c was 9.5 (standard deviation [SD], 2.5; range, 4.8–14.4). Mean BMI among the population sample was 33.2 kg/m2 (SD, 8.0 kg/m2); BMI for males was 31.4 kg/m2 (SD, 7.6 kg/m2) and for females was 35.5 kg/m2 (SD, 8.2 kg/m2).
Baseline food security scores were calculated using the US Household Food Security Survey Module developed by the US Department of Agriculture11 and are summarized in Table 2. The average score was 2.5 (SD, 2.3); 52% of participants had low or very low food security.
Baseline Health Data and Food Security
Baseline health maintenance data are presented in Table 3.
Baseline Health Maintenance Data*
Care Coordination Status
Care coordination status for patients before the intervention was assessed through their PCP, emergency department, or free clinic usage. In the initial survey, 93% of participants did not have a PCP; 91% answered affirmatively that they wanted a PCP. The mean reported emergency department visits/patient within the previous 9 months was 0.75 (range, 1–8 visits), whereas the mean number of reported free clinic visits/patient was 1.9 (range, 1–9 visits).
Linkage to FQHC
All 68 participants underwent the educational intervention and were referred for appointments at FQHCs. Of these 68 participants, 46 (68%) made an initial appointment, which varied between the 2 FQHCs: 59% (27/46) referred to FQHC1, and 86% (19/22) of patients referred to FQHC2 scheduled an initial appointment (P = .02).
Of the initial group of participants, 47% attended 1 appointment; 38% attended ≥2 appointments. When sites were compared, significantly more participants attended FQHC2 for ≥2 appointments (64% for FQHC2 vs 26% for FQHC1; P = .003). Participants assigned to FQHC2 made more appointments during their 9-month action period than those assigned to FQHC1 (mean visits per patient, 4.9 at FQHC2 vs 3.5 at FQHC1; P = .05). Demographics were not found to be confounders.
Barriers
The most common barriers to accessing health care through PCPs included no health insurance (85.3%), cost of medical care (72.1%), seldom or never get sick (25.0%), recently moved into area (22.1%), and unaware of where to seek care (20.6%). We were unable to assess whether these barriers changed through the linkage process as a result of a lack of responses to follow-up surveys (5 of 68 participants).
Hemoglobin A1c
There was a statistically significant decrease in HbA1c among participants attending ≥2 FQHC appointments during the 9-month action period (P = .008). Among these 21 participants, the baseline HbA1c was 9.5 (SD, 2.3) compared with an HbA1c value of 8.3 (SD, 2.2) after the action period. There was no statistical difference in the change in HbA1c between FQHC1 and FQHC2. These data are represented in Table 4. Only participants with values both before and after the action period were included in this analysis.
HbA1c at Baseline versus After the Action Period
Body Mass Index
There was a statistically significant increase in BMI among participants attending <2 FQHC appointments (P = .04). This group's baseline mean BMI was 32.9 kg/m2 (SD, 8.1 kg/m2) and increased to 33.4 kg/m2 (SD, 8.2 kg/m2) after the 9-month action period. This analysis was conducted for participants with BMI values before and after the action period that were available during chart review (n = 19).
Discussion
The key finding from our study was that expedited referral and a 1-on-1 educational intervention resulted in the linkage of participants to FQHCs and improved glycemic control.
Improved Linkage to FQHCs
We observed that 68% of participants scheduled an initial appointment with a FQHC, surpassing the historic 10% rate for patients at the PFC. Furthermore, we showed that 38% of individuals used the FQHC as their PCP, attending ≥2 appointments over the 9-month period. We concluded that educational interventions and expedited referrals are useful for patients to overcome barriers to accessing health care through FQHCs.
Our study identified and addressed some barriers previously described by HealthyPeople 2020 as critical components of the social determinants of health.12 Specifically, the 2 most common barriers for our population, lack of health insurance and concerns about cost of care, were addressed directly in our educational interventions. Our FQHC partners supported statements to the patients that they did not need insurance to be seen at these locations and that the cost of the visits would be assessed on a sliding scale based on ability to pay.
Univariate analysis indicated that the number of appointments at FQHC2 was significantly higher than at FQHC1, and demographics were not confounders. FQHC1 reported an average sliding fee of $30, whereas at FQHC2 the average fee was $10. Given that 72.1% of participants listed cost of medical care as a prominent barrier to primary care access, we attributed the greater success of linkage at FQHC2 to lower cost. In addition, we noted that the care coordinator at FQHC2 was more persistent in contacting participants to schedule appointments (up to 5 phone calls and 4 mailed follow-up letters vs up to 4 phone calls at FQHC1). Ramirez-Zohfeld et al13 reported <25% of underserved patients with diabetes who were contacted by phone or mail completed an appointment at an FQHC, identifying difficulties in reaching patients and engaging patients in care as contributing factors. These findings identify the need to maximize communication and the relationship between patient and provider.
Improved Diabetic Health
We observed a significant improvement in glycemic control as a decrease in mean HbA1c among participants who attended ≥2 appointments at FQHCs. By contrast, participants who did not use the FQHC as their primary provider did not have a significant improvement in glycemic control, even though they had a mean of 1.9 free clinic visits (SD, 0.98 visits) at the 9-month follow up. Although a few studies have shown that underserved patients can achieve control of chronic conditions such as diabetes under the care of free clinics, this seems to be possible when continuity of care is achieved, since their participants visited the free clinics on average >5 times in a 12-month period.14,15 Hence we attribute the improved glycemic control found in this study in part to physician–patient relationships during continuous care.
We surmise that improved adherence to medication regimens is also of particular importance. As shown in Table 3, before the intervention, participants reported not taking their medications on a regular basis. Anecdotally, we observed that these patients relied on the free clinic for medical attention and access to necessary medications. Naturally, with the structure and high patient volumes at these clinics, routine appointments for refills are challenging to obtain and can lead to gaps in medication adherence. In fact, one third of our participants had not taken their diabetes medications in the week before enrollment. Linkage with an FQHC should allow patients to be seen at regular intervals with improved access to prescriptions, allowing for better adherence.16 Furthermore, it was previously demonstrated that educational interventions alone can lead to improved HbA1c values.17 Thus the improved glycemic control shown in our study could be related to the education provided at the time of the initial intervention and at the primary care visits. Gorrindo et al18 demonstrated that a medical student health educator program at a free clinic facilitated HbA1c improvement 1 year after enrollment, despite inherent difficulties in caring for underserved patients.
Also during this study, patients who did not use the FQHC as their primary provider showed a trend of increased BMI, whereas patients who attended ≥2 FQHC appointments did not. We believe that without appropriate intervention, this low-SES population with diabetes follows a trend of increasing weight over time, such as that shown by Kahn et al.19 Further study is needed because our intervention did not include behavioral counseling specifically targeted at preventing weight gain.
Implications and Limitations of the LINKED Study
To our knowledge, this is the first study to explore the potential of linking patients with chronic conditions at free clinics to FQHCs and tracking health outcomes. However, it does have several limitations. First, the scale of the study was small and localized to 2 specific free clinics, both of which affect its external validity and generalizability. The follow-up survey data were difficult to obtain despite multiple attempts to reach participants; this has been found by others.13 Last, diabetic health outcome data were not available for all the initial participants, and these were especially challenging to obtain for participants who did not attend appointments at FQHCs, which may have resulted in attrition bias.
Future directions include extrapolating this study design to other chronic conditions commonly seen at free clinics, such as hypertension. In addition, analyses of the potential reduction in the number of emergency department and free clinic visits, and the corresponding impact of linkage programs on overall health care spending, would be valuable.
Conclusion
The LINKED study demonstrated improved linkage to FQHCs after expedited referral and 1-on-1 educational interventions by medical students. This intervention described the importance of having a PCP and addressed 2 major barriers to primary care: lack of health insurance and cost of medical care. In addition, this study demonstrated improved glycemic control among patients using the FQHC as their PCP. These results support the implementation of similar linkage programs between free clinics and PCPs.
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely thank all the members of the LINKED team for participating in patient education, recruitment, and initial data collection: Krystin Bachman, Stephanie Carlson, Edward Cheng, Jennifer Cooperrider, Edward Cuaresma, Gina Ferris, Brian Ichwan, Dacey Jackson, Lua Jafari, Alisha Moreno, Scott Morton, Brittany Shrefler, and Richard Tang. The authors also thank Daniel Clinchot, MD, for his guidance; Lorraine Wallace, PhD, for making comments on the manuscript; Jennifer Lehman, of the Ohio State University Department of Family Medicine, for assistance with REDCap; Isi Ikharebha, Executive Director of the PFC; Paula Dunn, Administrative Director of the PFC; Dr. Nathan Yost, physician-volunteer at the PFC; the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Medical Student Steering Committee of the CFC; Buhari Mohammed, MD, of the Columbus Neighborhood Health Center; Dana Vallangeon, MD, of the Lower Lights Christian Health Center; and the FQHC coordinators, Kimberly Salzwedel and Shaton Tucker.
Notes
↵* These authors contributed equally to this work.
This article was externally peer reviewed.
Funding: Funding was received from the Ohio State University Department of Family Medicine, the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Alumni Association, and the Bennett Research Scholarship. In addition, REDCap is supported at our institution by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (grant no. 8UL1TR000090-05).
Conflict of interest: none declared.
- Received for publication August 14, 2015.
- Revision received December 2, 2015.
- Accepted for publication December 7, 2015.